Groundwater Depletion in Punjab
Battling the Threat of Groundwater Depletion in
Punjab
Punjab, known as the breadbasket of India, has been facing a
grave concern in recent years - the accelerating rate of groundwater depletion.
This issue has raised alarms among farmers and experts, as it poses a
significant threat to the agricultural sector, the livelihood of farmers, and
the overall ecological balance of the region. This article delves into the
causes, consequences, and potential solutions to address the worrisome problem
of groundwater depletion in Punjab.
The Scale of the Problem:
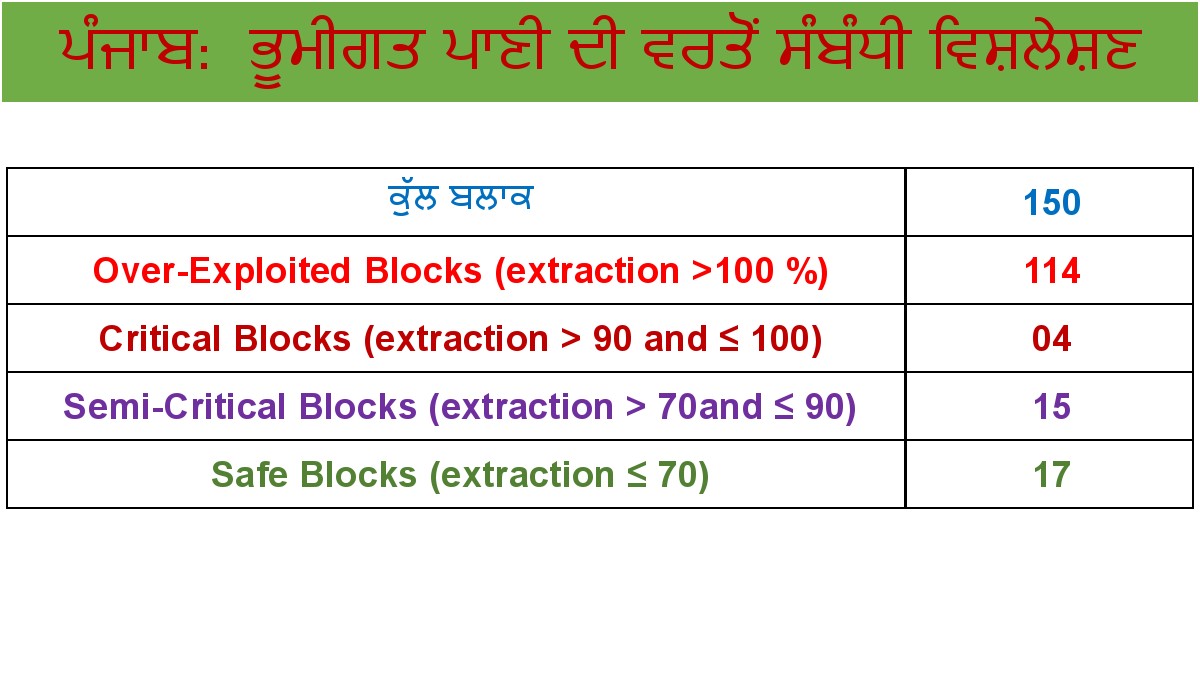
The severity of groundwater depletion in Punjab cannot be
overstated. Over the years, excessive groundwater extraction for irrigation
purposes has resulted in a significant drop in water levels, leading to a state
of crisis. According to studies, the groundwater table has been declining at an
alarming rate of about 0.5 meters per year in several parts of the state.
Agricultural Practices and Water Demand:
One of the primary factors contributing to groundwater
depletion in Punjab is the intensive agricultural practices prevalent in the
region. The cultivation of water-intensive crops, such as paddy and wheat,
coupled with the reliance on inefficient irrigation methods, has significantly
increased the demand for groundwater. The overexploitation of this vital resource
has pushed the ecosystem to its limits.
Impact on Farmers:
The depletion of groundwater has severe implications for
farmers in Punjab. As water levels drop, farmers face difficulties in accessing
adequate irrigation water for their crops. This leads to reduced agricultural
productivity, increased dependence on expensive alternatives like diesel pumps,
and financial burdens for farmers. The cycle of debt and distress is
exacerbated by the need to drill deeper borewells, resulting in higher costs
and further depletion of groundwater.
Environmental Consequences:
The rapid depletion of groundwater in Punjab has
far-reaching environmental consequences. The decline in water levels affects
the health of rivers, wetlands, and ecosystems dependent on groundwater. It
disrupts the natural balance, reduces water availability for wildlife, and
threatens biodiversity. Additionally, the excessive extraction of groundwater
can lead to land subsidence, soil degradation, and increased salinity, further
compromising agricultural sustainability.
Role of Government and Policy Interventions:
Addressing the groundwater depletion crisis in Punjab
requires a multi-faceted approach. The government has a crucial role to play in
implementing effective policies and regulations to manage water resources
sustainably. This includes promoting water-efficient irrigation techniques,
encouraging crop diversification, incentivizing the adoption of groundwater
recharge measures, and strict enforcement of regulations on groundwater
extraction.
Community Participation and Awareness:
Community participation is vital in tackling the issue of
groundwater depletion. Farmers need to be educated about sustainable water
management practices and provided with technical support and resources to
implement them. Creating awareness among the general public about the
importance of water conservation and the need to conserve groundwater is also
crucial for long-term solutions.
Embracing Sustainable Farming Practices:
Promoting sustainable farming practices, such as precision
agriculture, micro-irrigation systems, and organic farming, can significantly
reduce water consumption and mitigate the effects of groundwater depletion.
These practices focus on optimizing water usage, improving soil health, and
reducing reliance on chemical inputs, ensuring long-term agricultural
sustainability.
In the issue of groundwater depletion in Punjab, teachers
can play a significant role in raising awareness and promoting sustainable
practices among students and the community. Here are some actions teachers can
take:
Incorporate Environmental Education: Integrate environmental education into the
curriculum, emphasizing the importance of water conservation, sustainable
farming practices, and the consequences of groundwater depletion. Teach
students about the water cycle, the value of water resources, and the impact of
human activities on the environment.
Organize Awareness Campaigns: Collaborate with students, parents, and local
organizations to organize awareness campaigns and events focused on water
conservation. Conduct workshops, seminars, and presentations to educate the
community about the issue of groundwater depletion, its causes, and the need
for sustainable water management.
Promote Sustainable Farming Practices: Educate students about sustainable farming techniques
that reduce reliance on groundwater, such as drip irrigation, rainwater
harvesting, and crop rotation. Encourage students to implement these practices
in school gardens or community farming projects.
Foster a Conservation Mindset: Instill in students the importance of water
conservation in their daily lives. Teach them practical tips, such as taking
shorter showers, turning off taps when not in use, and collecting and reusing
rainwater. Encourage students to be mindful of their water usage and to spread
awareness among their families and peers.
Conduct Research and Projects: Encourage students to conduct research projects on
water conservation, groundwater management, and sustainable agriculture.
Support them in collecting data, analyzing findings, and presenting their
results to create a deeper understanding of the issue and potential solutions.
Engage in Community Partnerships: Collaborate with local government bodies, NGOs, and
environmental agencies working on water conservation initiatives. Encourage
students to participate in community service projects related to water
conservation, such as cleaning water bodies, planting trees, or organizing
awareness drives.
Advocate for Policy Changes: Teachers can become advocates for policy changes at
the local and state levels. Engage with policymakers, participate in relevant
forums, and voice concerns about the depletion of groundwater resources. Lobby
for stricter regulations on water extraction and the promotion of sustainable
water management practices.
Lead by Example: Teachers
can demonstrate sustainable practices in their own lives and classrooms. Model
water conservation behaviors, such as using water-efficient fixtures, recycling
water, and minimizing waste. By practicing what they preach, teachers can
inspire students to adopt responsible water usage habits.
The accelerating rate of groundwater depletion in Punjab is
a matter of great concern for farmers, experts, and policymakers. It threatens
the very foundation of agriculture, livelihoods, and the environment.
Addressing this issue requires a collective effort, involving government
interventions, community participation, and the adoption of sustainable farming
practices. By implementing effective policies, raising awareness, and promoting
responsible water management, Punjab can strive towards a more sustainable
future, ensuring the availability of water resources for generations to come. By
taking these steps, teachers can contribute to a collective effort in
mitigating groundwater depletion in Punjab. Their influence on students can
empower the next generation to become informed and responsible stewards of
water resources, ensuring a sustainable future for the state.